Terminology and Information related to SNJ Lasers.
Studied by
Austin Sungkon Lim
LASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation)
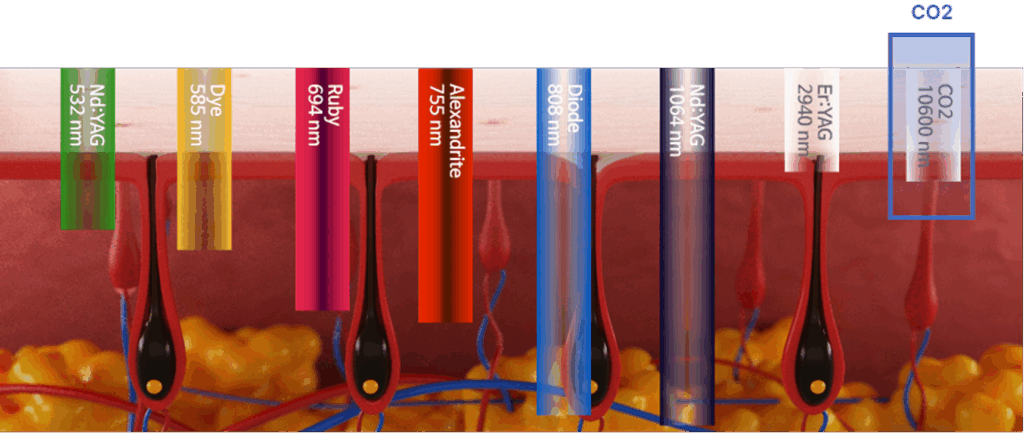
- Nd:YAG 532 nm wavelength(nm)
- Dye 585 nm
- Ruby 694 nm
- Alexandrite 755 nm
- Diode 808 nm
- Nd:YAG 1,064 nm
- Er:YAG 2,940 nm
- CO2 10,600 nm wavelength(nm)
- Milli-second (ms)=refers to a duration of one thousand of second
- Micro-second (us)= refers to a duration of one million of a second
- Nano-second (ns)=refers to a duration of one billionth of a second
- Pico-second (ps)=refers to a duration of one trillionth of a second
Epidermis → Dermis → Subcutaneous fat >>> SMAS
- Wart =사마귀
- Rosacea=빨간코 (로쎄이시아)
- Melasma=기미
- Telangiectasia=말초혈관 확장증 (텔렌지엑티시아)
- Acne =여드름
- Flush=hot flush= 홍조, 열감
- Freckle=주근깨
- Seborrheic Dermatitis (세브리익 더마타이티스) = 지루성 피부염
- Café-Au-Lait-Spot=(CALS)밀크커피색반점, 담갈색반점 (케페이레잇스팟)
- Lentigines (렌티진스)=Lentigo (렌타이고)=검은 사마귀, 흑색점
- Liver spot = 검버섯 =age spot
- Nevus (네버스) =모반 (Blue nervus=청색모반)
- Tattoo
- Wrinkle (fine wrinkle)
- Vitiligo = 백반, 백피
- Fine blood vessel, thin blood vessel=미세모세혈관
- Scar (ice pick scar, rolling scar, boxed scar, linear scar, acne scar)
- LIOB=Laser Induced Optical Breakdown
- PIH = Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation =염증으로 인해 발생되는 색소침착
- Erythema= 홍반, acne erythema
- Carbon peeling=good for oily skin, enlarged or clogged pores, light wrinkles, acne spots, sunspots, age spots, skin sagging, by activated charcoal which is used for skin rejuvenation
- Mole = 점
- Corn = 티눈
- Soft fibroma(파이브로마) = 연성 섬유종, 쥐젖, 섬유상피 용종, 피부폴립
- Milium = 비립종, 좁쌀종, 흰 좁쌀 모양
- Syringoma = 땀관종 (한관종)
- Sebaceous gland (피지샘) 쓰베이셔스 글랜
- Abnom (Acquired Bilateral Nevus of Ota-like Macule) is common pigmentary condition in Asians.
- Chromophores: Light energy is absorbed by different objects within the skin, these objects called “chromophores”, the main chromophores in the skin are Melanin, Hemoglobin, Water, Lipid.
- Melanin: is responsible for skin color and protects against harmful UV radiation.
- Hemoglobin: found in red blood cells, contributes to skin color, hemoglobin is essential for oxygen transport and gives skin its reddish hue.
- Water =Human body
- Lipids (지방질): including fats and oils
- Chromophores in the skin: Pigment (Melanin), Blood (Hemoglobin), Water, Lapid (oil & fat)
- Hemostasis (히머스테이시스) = 지혈
- Coagulation (코아귤레이션) = 응고, coagulation time =응고시간
- Evaporation = 증발
- Incision = 절개
- Excision = 적출(제거)
- Skin resurfacing & rejuvenation
- Skin revitalization =피부활력
- Scar improvement
- Skin whitening, brightening
- Pore tightening
- Soft peeling
- Fine wrinkle improvement
- Ablative laser =이산화탄소, CO2 Laser
- Non-ablative laser=비파괴 레이저, IPL (Intense Pulse Light), BBL (Broadband Light), Pulsed Dye Laser)
- Vaginal tightening & rejuvenation
- Urinary incontinence improvement
- Labia brightening
- Skin booster = Dr. Lucent mask
- Adjacent (어제이슨)=인접한, 가까운 mitigate = 완화시키다
- Hypertrophic scar =비대성 흉터, 상처가 회복되는 과정에서 생기는 흉터, 원래 상처의 경계를 넘어 확장되며 두께와 색상이 변화합니다.
- Melanocytic nevus: 멜라노사이릭 너비스=멜라닌 색소세포성 모반(점)
- Seborrheic keratosis(서브레이크 케라토시스): 지루각화증 (검버섯, 노령층에서 흔히 발생)
- Convex lesions(볼록한 병변) on the face, 볼록한=concave
- TRT (Thermal Relaxation Time): the TRT of water on the CO2 laser is 800us or less.
- TRT refers to the time it takes for the temperature to decrease by half (50%) after laser irradiation.
The CO2 laser wavelength (10,600nm) is predominantly absorbed by water, which is the primary chromophore.
This absorption makes CO2 lasers highly effective for procedures involving tissues with high water content, such as in:
- Aesthetic treatments (skin resurfacing, wrinkle reduction).
- Surgical applications (cutting, vaporization, and coagulation of tissues).
- Veterinary and medical uses (soft tissue surgery).
- Finexel (Co2 laser), wavelength: 10,600nm, Mode structure: Gaussian, Pulse frequency: 1~990Hz, Pulse duration time: 50~2,000 us, aiming beam: laser diode 5mW pilot beam (650nm), Fractional: 1×1~20×20, Delivery system: 7-joint balanced articulated arm, Density: 0.1mm~2.0mm
- Finexel has high peak power as 300 Watts with Ultra Pulse.
It makes less thermal damage on skin tissues so that patients feel less pain and get faster recovery, called pinhole method.
The term “CO2 Laser Ultra Pulse frequency 990Hz” refers to the pulse rate or repetition frequency at which the CO2 laser operates in Ultra Pulse mode.
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
- CO2 Laser: This is a type of gas laser that uses carbon dioxide as the medium to produce infrared light, typically in the 10,600 nm wavelength range.
CO2 lasers are commonly used in medical, surgical, and veterinary applications for cutting, vaporizing, and coagulating tissues. - Ultra Pulse Mode: Ultra Pulse is a mode of operation where the laser emits energy in extremely short, high-power bursts (pulses). This allows for very precise, controlled cutting or ablation with minimal thermal damage to surrounding tissues.
- Frequency (990Hz): The frequency here (measured in Hertz or Hz) indicates how many pulses are being emitted per second. In this case, 990 Hz means the laser is pulsing 990 times per second. This high-frequency pulsing allows for smooth tissue interaction, enhancing precision and reducing damage.
In summary, Ultra Pulse frequency of 990 Hz suggests that the laser emits rapid, controlled bursts of energy at 990 pulses per second, which is ideal for delicate procedures requiring precision and minimal collateral damage.
- Finexel fractional max energy: 300mJ, max overlap:10, Max scan area: 20mm x 20mm
- Finexel fractional CO2 laser treatments are used for indications such as large pores, scars, wrinkles and skin tightening.
- Finexel treatment density can be adjusted by the distance (mm) between beams. Shorter distances result in higher density, while longer distances lead to lower density.
- Finexel Light Treatment: low energy, low density and fewer passes.
- Finexel Intense Treatment: high energy, higher density and more passes.
- Finexel handpiece (fractional, surgical, vaginal)
- Finexel : ablative fractional laser handpiece spot size:
Stanadard: 100um = 0.1mm
Option: 80um =0.08mm, 180um = 0.18mm, 500um = 0.5mm - Finexel irradiate high pick powers around 300 watts with ultra-pulse.
It minimizes thermal damage on adjacent tissues so that patients mitigate pain and recover faster. - Finexel stacking: 1~10, (energy 50mJ, stacking:1) vs (energy 10mJ, stacking: 5)
- Finxel fractional shapes (square, triangle, circle), patterns (standard, random, scatter)
- Finexel surgical handpiece: f-100mm spot size:0.4mm,
f-50mm spot size:0.2mm
The Microscopic Treatment Zone (MTZ) is a key concept in fractional CO2 laser therapy.
MTZ refers to the tiny, controlled areas of thermal damage created by the laser on the skin’s surface.
Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Definition of MTZ
- MTZs are small, precise columns of tissue that are vaporized or thermally coagulated by the laser during treatment.
- These zones are surrounded by untouched, healthy skin, which plays a crucial role in the skin’s rapid healing process.
2. How MTZ Works in Fractional CO2 Laser
- Fractional CO2 lasers use a pattern of microbeams or dots to deliver energy to the skin.
- Each microbeam targets specific skin areas, creating thousands of MTZs in a grid-like pattern.
- The size, depth, and density of these MTZs depend on the laser’s settings, such as energy level, pulse duration, and spot density.
3. Benefits of MTZ in Skin Rejuvenation
- Controlled Injury for Collagen Remodeling: The controlled thermal damage stimulates the production of new collagen and elastin, essential for skin tightening and rejuvenation.
- Fast Recovery: Because only a fraction of the skin is treated, with healthy skin left intact between MTZs, the recovery time is shorter compared to non-fractional treatments.
- Customizable Treatment: The size, density, and depth of MTZs can be adjusted to target specific skin concerns, such as wrinkles, scars, pigmentation, or texture irregularities.
- Improved Safety: The precision of MTZs minimizes the risk of side effects like prolonged redness or pigmentation changes compared to traditional CO2 lasers.
4. Applications of MTZ in Aesthetic Treatments
- Wrinkle Reduction: Enhances skin firmness and elasticity.
- Scar Treatment: Reduces acne scars, surgical scars, and other textural issues.
- Pigmentation: Addresses sunspots, melasma, and other forms of hyperpigmentation.
- Overall Skin Rejuvenation: Improves skin tone, texture, and appearance.
5. Key Parameters Affecting MTZ
- Depth: Determines how deep the laser penetrates. Deeper MTZs are used for scars or wrinkles, while shallower MTZs target pigmentation or fine lines.
- Density: Refers to the number of MTZs per unit area. Higher density offers more aggressive treatment but may require longer downtime.
- Pulse Energy: Higher energy creates larger MTZs, while lower energy produces finer MTZs.
6. Healing Process of MTZ
- After treatment, the MTZs undergo a natural healing process:
- Day 1-3: Epidermal repair begins as new cells migrate to close the treated zones.
- Day 3-7: The skin regenerates, and peeling or crusting might occur as old, damaged skin is shed.
- Weeks 1-4: Collagen remodeling continues, improving the skin’s structure and appearance.
- Months 1-6: Gradual improvement in skin texture and elasticity.
Understanding MTZ helps patients and practitioners tailor fractional CO2 laser treatments for optimal results, balancing effectiveness with safety and recovery.
- Verruca Plana (평편사마귀): pin hole method, 990Hz, 300us, single, focusing, f-50,
f-100 H/P. - Finexel Evero =vaginal tightening, collagen stimulation
- Finexel scan area:1×1~20mm x 20mm
- Finexel weight:110 lbs, Max power: 30W, pixel energy: 5~300mJ, overlap:1~10
- Finexel parameter for major indications: Fractional mode & CO2 mode (surgical) & Evero mode
- Comparison for CO2 Laser vs Er:YAG Laser
- Finebeam Qplus : Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser (532nm & 1064nm)
- Finebeam Dual : Q-Switched & Long-Pulsed Nd:YAG Laser (532nm, 1064nm with Long-Pulse)
- 1064nm & 532nm Zoom Collimation handpiece: all applications in general (toning, carbon peeling and others, 532nm: 1~7mm, 1064nm: 2~10mm spot size
- 1064nm DOE QSW fractional handpiece: pigment care, QSW 1064nm : spot 7mm, top hat beam profile.
- 1064nm Zoom MLA QSW handpiece: Elastisity related care, QSW 1064 : spot size 4mm, 7mm, 10mm, gaussian beam profile, good for LIOB effect
- 650nm Ruby handpiece: Rosacea, fine blood vessel, green tattoo, QSW 1064: 3mm (DYE HP)
- 595nm Gold handpiece: Vascular melasma, rosacea, purple & sky-blue tattoo, 1064 QSW: 5mm (DYE HP)
- Indications for Q-Switched: Melasma & PIH improvement, soft peeling, tattoo removal, freckle, lentigines, café-au-lait spot, becker’s nevus, age spot improvement.
- Indications for Long-Pulsed: Genesis, skin tightening & lifting, Acne erythema improvement, Telangiectasia, Hair removal.
- Fibroblast: 섬유아세포: They play crucial roles in maintaining skin health and function.
- Genesis (1064nm long-pulse) treatment is the way to activate fibroblast of papillary dermis (유두진피), increase collagen composition, improve solar elastosis(일광탄력섬유증), decrease inflammation cytokine.
- Genesis treatment effective for whitening such as melasma and other pigments associated solar elastosis caused by long term UV exposure
- Genesis treatment effective for tightening such as skin texture, pore size, wrinkle.
- Finebeam Zoom MLA handpiece (Micro Lens Array): Gaussian distribution, LIOB effect for skin rejuvenation, 120 Micro lenses, 3mm, 7mm, 10mm spot size, good for acne scar, pore size, skin laxity, skin texture, fine wrinkle, dermal pigments.
10mm has 100 effective spot, 3mm spot setting is good for acne scar, small scar. - Finebeam DOE handpiece (Diffractive Optic Element): top hat beam profile, uniform fractional beam, minimizing the risk of side effects and downtime, good for toning for sensitive skin, easy pigmentation rebound skin and thermal sensitive skin, seborrheic dermatitis (지루성 피부염), pigmented lesions (색소가 있는 병변)
- Finebeam 2.2J PDP Mode (Photoacoustic Double Pulse) 1,100mJ x 2): most effective in dermis area without epidermis skin damage, generate photoacoustic effect enough to break melanin and tattoo ink in the dermis area, optimal results for pigment in dermis such as Melasma, Abnom, Tattoo.
- Finebeam Dual: Q-Switched (nanosecond), Quasi (microsecond), Long-Pulsed (millisecond)
- Dual toning(1064nm): Toning with Q-Switched → Genesis toning with long-pulsed
- Tri full toning(1064nm): Toning with Q-Switched → Genesis toning with long-pulsed → MLA with Q-Switched
In a Q-Switched Nd:Yag laser, the term “Ontime” refers to the duration during which the laser actively emits light within a single pulse cycle.
It represents the time period when the laser energy is delivered to the target tissue in a controlled burst.
Key Aspects of “Ontime”:
- Pulse Duration:
- The Ontime is closely related to the pulse duration, which is critical in determining how energy is delivered to the skin or tissue.
- In Q-switched lasers, pulses are extremely short (in nanoseconds or picoseconds), delivering high peak power for effective treatment.
- Therapeutic Impact:
- Short Ontime durations allow for precise energy delivery, minimizing heat diffusion to surrounding tissues.
- It ensures the laser targets specific chromophores (e.g., melanin, tattoo ink) without causing significant damage to nearby areas.
- Adjustability:
- Some devices allow adjustment of the Ontime to customize treatment for different skin types or conditions (e.g., pigmentation, tattoos, or vascular lesions).
Understanding Ontime helps in optimizing treatment efficacy and safety when using Q-switched Nd:YAG laser.
1. Energy (Measured in Joules, J)
- Definition: The total amount of laser energy delivered per pulse.
- Meaning:
- It refers to the absolute amount of energy emitted by the laser in a single pulse.
- Usage:
- Important for understanding the overall energy output of the laser system.
- Helps in determining the power delivered in specific applications.
2. Fluence (Measured in Joules per square centimeter, J/cm²)
- Definition: The energy per unit area delivered to the target.
- Formula: Fluence = energy (J) / spot size area (J/cm2)
- Spot Size Area is the surface area of the laser’s beam at the point of contact.
- Meaning:
- Fluence describes how concentrated energy is when it reaches the skin or tissue.
- A higher fluence means more energy is delivered per unit area, which increases the intensity of the treatment.
- Usage:
- Crucial in determining the treatment’s effectiveness and safety.
- Different applications (e.g., tattoo removal, hair removal, skin rejuvenation) require specific fluence levels to target chromophores without damaging surrounding tissues.
total energy remains the same, the fluence changes depending on the spot size.
In the context of Nd:YAG lasers, “off time” refers to the interval between laser pulses when the laser is not emitting energy.
The 1064nm PDP mode refers to a specific operating mode of a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser that uses a wavelength of 1064 nanometers in conjunction with Photoacoustic Double Pulse (PDP) technology.
This mode is particularly used in advanced laser systems for targeted treatments such as tattoo removal, pigmentation treatments, and skin rejuvenation.
Below is a detailed explanation:
Key Features of 1064nm PDP Mode
- Wavelength (1064nm):
- Penetration Depth: The 1064nm wavelength penetrates deeper into the skin compared to shorter wavelengths like 532nm.
- Target Chromophores:
- It is highly effective in targeting melanin in deeper skin layers and tattoo inks (especially black, dark blue, and green colors).
- It also interacts with hemoglobin, making it suitable for vascular lesions.
- PDP Mode (Photoacoustic Double Pulse):
- Double Pulse Delivery: PDP mode delivers two sequential pulses within a very short interval.
- Photoacoustic Effect:
- The first pulse creates a photoacoustic wave that breaks down larger pigment particles.
- The second pulse follows immediately, targeting the fragments for further breakdown.
- This sequential action enhances the fragmentation of pigments or ink particles, improving treatment efficacy.
- Advantages of PDP Mode:
- Improved Efficacy: By delivering two pulses in quick succession, PDP mode achieves a more thorough and efficient breakup of target particles.
- Reduced Risk of Side Effects: The energy is distributed between two pulses, reducing the likelihood of overheating or damaging surrounding tissues.
- Enhanced Skin Rejuvenation: The dual pulses stimulate collagen remodeling, making it effective for skin rejuvenation treatments.
- Minimized Downtime: The reduced thermal effect decreases post-treatment redness and swelling.
Applications of 1064nm PDP Mode
- Tattoo Removal:
- Particularly effective for dark inks (black, dark blue, green).
- Suitable for tattoos located in deeper layers of the skin.
- Pigmentation Treatment:
- Treats melasma, nevus of Ota, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Targets deep dermal pigmentation effectively.
- Vascular Lesions:
- Useful for treating conditions like telangiectasias, spider veins, and hemangioma (혈관종).
- Skin Rejuvenation:
- Stimulates collagen production and reduces the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and large pores.
Summary
The 1064nm PDP mode is a powerful and versatile tool in the field of dermatology and aesthetics.
Its ability to deliver double pulses with a deep-penetrating wavelength makes it highly effective for various treatments, including tattoo removal, pigmentation, vascular lesions, and skin rejuvenation.
The PDP mode enhances treatment outcomes while minimizing risks and downtime, offering a superior patient experience.
Key Differences: Quasi-Mode vs. PDP
| Feature | Quasi-Mode | Photoacoustic Double Pulse (PDP) |
| Energy Delivery | Short, high-energy pulses in microseconds | Two rapid pulses with nanosecond intervals |
| Mechanism | Thermal effect (heating target tissue) | Photoacoustic effect (mechanical disruption) |
| Pulse Duration | Microsecond to millisecond range | Nanosecond range |
| Effect on Tissue | Controlled heating for coagulation/remodeling | Mechanical disruption of particles or granules |
| Applications | Hair removal, skin rejuvenation, vascular/pigmented lesions | Tattoo removal, pigment fragmentation, scar treatment |
| Thermal Impact | Moderate heating, deeper tissue penetration | Minimal thermal diffusion, surface-level precision |
| Penetration Depth | Deep penetration for targeting dermal layers | Surface-to-mid dermal targets (shallow focus) |
| Precision | General chromophore targeting | Precise particle targeting (e.g., pigment granules) |
Fitzpatrick Skin Types
| Skin Type | Description | Tanning & Burning Reaction | Typical Characteristics | Examples |
| Type I | Very fair, pale white skin | Always burns, never tans | – Very sensitive skin – Often with freckles – Red or blonde hair, blue/green eyes | Northern European (e.g., Irish, Scandinavian) |
| Type II | Fair skin | Usually burns, tans minimally | – Sensitive to sun – Light hair and eyes | Central European, some Caucasians |
| Type III | Medium, beige skin tone | Sometimes burns, tans gradually to light brown | – Average sun sensitivity – Darker hair and eyes | Southern European, fair-skinned Asians |
| Type IV | Olive or light brown skin | Rarely burns, tans easily | – Minimal sun sensitivity – Darker hair and eyes | Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, Hispanic |
| Type V | Brown skin | Very rarely burns, tans darkly | – Sun-insensitive – Darker skin and features | South Asian, some African and Middle Eastern |
| Type VI | Deeply pigmented dark brown/black skin | Never burns, deeply pigmented | – Highly sun-insensitive – Richly pigmented | African, Aboriginal, Afro-Caribbean |
Hyperpigmentation in CO₂ laser practice refers to an unwanted darkening of the skin in the treated area.
It happens when the laser procedure triggers the skin to produce excess melanin (the pigment responsible for skin color).
This condition is typically called Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH).
Why It Happens
- Inflammatory Response – The CO₂ laser creates controlled thermal injury in the skin. In some patients (especially those with darker skin types), this injury stimulates melanocytes to overproduce melanin.
- Sun Exposure After Treatment – UV radiation after laser treatment greatly increases the risk of PIH.
- Improper Laser Settings – Too much energy, overly aggressive passes, or insufficient cooling can cause deeper or excessive damage, increasing the chance of pigment changes.
- Patient’s Skin Type – Fitzpatrick skin types IV–VI (medium to darker skin tones) are more prone to hyperpigmentation.
- Inadequate Aftercare – Not following post-laser instructions (like using sunscreen, avoiding heat/irritation, or not applying prescribed creams) may worsen pigmentation.
Types of Pigment Changes After CO₂ Laser
- Hyperpigmentation (dark spots) – more common, especially in darker skin.
- Hypopigmentation (light patches) – less common but can occur if melanocytes are destroyed.
Prevention & Management
- Pre-treatment preparation: Topical agents (like hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C) may be used before the procedure in high-risk patients.
- Post-treatment sun protection: Daily broad-spectrum sunscreen is critical.
- Topical treatments: Lightening creams (hydroquinone, azelaic acid, kojic acid) may help reduce PIH.
- Avoid irritants: No picking, scratching, or harsh skincare products on treated areas.
- Medical management: In persistent cases, dermatologists may use additional chemical peels, microneedling, or fractional laser adjustments.
👉 In short, hyperpigmentation after CO₂ laser is usually temporary and can fade with time and treatment, but prevention through careful laser settings, patient selection, and strict aftercare is the most important.
In aesthetic CO₂ laser practice, PIH stands for Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation.
Meaning
- It is a darkening of the skin that develops after inflammation or injury caused by the laser.
- The CO₂ laser works by creating controlled microscopic injuries to resurface or rejuvenate the skin. In some cases, the healing process triggers the melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) to make excess melanin.
This results in brown or dark patches in the treated area.
Key Points in CO₂ Laser Context
- Common in darker skin types (Fitzpatrick IV–VI) but can occur in any skin tone.
- Usually appears days to weeks after treatment.
- It is generally temporary, though it may last for weeks to months if untreated.
- Prevention: careful energy settings, patient selection, and strict sun protection post-procedure.
- Treatment: topical depigmenting creams (hydroquinone, retinoids, vitamin C)
🌟 Preventing Dark Spots (PIH) After CO2 Laser Treatment
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH) means the skin may heal darker than normal after laser because of extra pigment (melanin).
The good news: with proper care, PIH can often be prevented.
✅ Before Your Treatment
- Avoid sun exposure: No tanning, sunbathing, or tanning beds for at least 2–4 weeks.
- Use sunscreen daily: Apply a broad-spectrum SPF 30–50+.
- Prepare your skin (if recommended by your provider): Lightening creams (such as hydroquinone) or retinoids may be used to calm pigment cells.
- No harsh treatments: Stop waxing, scrubs, or strong peels before treatment.
✅ Right After Treatment
- Protect your skin from the sun every day, this is the most important step.
- Keep skin moisturized: Use gentle creams or ointments to help heal.
- Avoid scratching or picking: Let your skin heal naturally.
- Follow your provider’s instructions on soothing creams or medicines.
✅ In the Healing Weeks
- Continue strict sun protection with SPF 50+ and protective clothing.
- Resume lightening creams (if advised) about 1–2 weeks after the skin has healed.
- Be patient: Healing takes time. Dark spots can often be avoided with careful care.
⭐ Key Tips
- Sun is the #1 enemy after CO2 laser, always block UV sunlight.
- Moisturize and protect your skin barrier.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions closely for best results.
What Is Wavelength?
- Wavelength is the length of one cycle of a repeating wave, such as light or sound.
- It is typically measured in nanometers (nm) or micrometers (μm).
- 1 μm = 1,000 nm
- Example: The Finexel CO₂ laser operates at a wavelength of 10,600 nm (10.6 μm).
Basic Principle of Wavelength
- The wavelength determines the type or color of light.
| Wavelength Range | Type of Light | Typical Use |
| 400–700 nm | Visible light (seen by eyes) | LED, IPL |
| 700–1400 nm | Near-infrared | Nd:YAG, Diode laser |
| 10,600 nm | Far-infrared (CO2 laser) | Tissue cutting, resurfacing, coagulation |
Laser Wavelength and Tissue Interaction
- Tissue absorption varies by wavelength.
- The 10,600 nm wavelength of CO2 lasers is highly absorbed by water.
- Since most tissues, mucosa, and skin contain water,
- This makes CO2 lasers effective for precise cutting, resurfacing, and coagulation.
Wavelength Selection Depends on Treatment Goal
| Wavelength | Primary Target | Example Devices |
| 532 nm | Melanin, blood vessels | KTP, IPL |
| 755 nm | Melanin | Alexandrite |
| 810–980 nm | Hair follicle, vessels | Diode |
| 1064 nm | Deep tissues, vessels | Nd:YAG |
| 10,600 nm | Water → Soft tissue cut | CO2 (e.g., Finexel) |
Summary
- Wavelength is the length of light and a key parameter that determines laser type and therapeutic effects.
- The Finexel’s 10,600 nm wavelength is strongly absorbed by water,
→ making it ideal for precise cutting, coagulation, regeneration, and resurfacing.
Wavelength (λ) vs. Pulse Duration (τ): Different Parameters
These are two separate physical properties:
| Parameter | Unit | Represents |
| Wavelength (λ) | nm or μm | Type of light & its absorption by tissue |
| Pulse Duration (τ) | μs–ms | How long the laser energy is emitted per pulse |
CO2 (10.6 µm) Laser Example
1) Wavelength (λ)
- Definition: The physical length of one wave cycle.
- In lasers: Determines which substance absorbs the energy best.
- CO2’s 10.6 µm is highly absorbed by water → ideal for skin, mucosa, and soft tissue cutting, vaporization, and coagulation.
- Formula:
- c = f × λ
- c: speed of light
- f: frequency
- λ: wavelength
- Longer λ → lower frequency
- c = f × λ
✅ Key Point: Wavelength determines the “target”. For CO2, the target is water.
2) Pulse Duration (τ)
- Definition: Duration that a single laser pulse is emitted.
- Measured in microseconds (μs) to milliseconds (ms).
- Controls how heat spreads in tissue → directly impacts:
- Incision sharpness
- Thermal damage zone
- Pain, bleeding, recovery
Related Concepts:
- PRR (Pulse Repetition Rate): How many pulses per second.
- Duty Cycle (D): Proportion of time the beam is on
D ≈ τ × PRR (e.g., 0.5 ms × 200 Hz = 10%) - Peak Power vs. Average Power:
- Energy per pulse: E = P_peak × τ
- Avg power: P_avg = E × PRR = P_peak × D
- Spot Size & Fluence:
- Fluence (J/cm²) = Energy / Area
- Shorter τ → Higher peak power → Better cutting/vaporizing, less heat diffusion
- Thermal Diffusion Length (L_th):
L_th ≈ √(4ατ)- α: thermal diffusivity (~1–1.5×10⁻⁷ m²/s)
- Example:
- τ = 1 ms → L_th ~ tens of μm → precise
- τ = 10 ms → L_th increases → more coagulation
✅ Key Point: Pulse duration determines “how localized the heat effect is”.
- Shorter τ → Less collateral damage
- Longer τ → More coagulation/hemostasis
3) Wavelength + Pulse Duration = Combined Effect
- Wavelength (10.6 µm) → Strong absorption by water → Energy is deposited near surface (optical penetration ~tens of μm)
- Short τ (tens–hundreds μs or few ms):
- Energy confined before heat spreads
- Clean cuts, minimal collateral heat damage
- Long τ (ms–tens of ms):
- Heat diffuses → Better coagulation/hemostasis, but more risk of charring or broader thermal injury
4) Fractional CO2 Laser & TRT Concept
- TRT (Thermal Relaxation Time):
TRT ≈ d² / (4α)- d: target diameter
- Energy should be delivered within TRT to localize heat and minimize spread
- Fractional CO2 (MTZ diameter ~tens to hundreds μm):
- Shorter τ → Thinner coagulation zone → Faster healing, reduced PIH risk
Finexel Technical Specs (Pulse Time)
- Wavelength: 10,600 nm
- Modes: Fractional, Continuous Wave (CW), Ultra Pulse
- Pulse Duration: 50 ~ 2,000 μs (i.e., 0.05 ~ 2.0 ms)
